What Size Opening Can A Mouse Get Through
Mouse Facts: Habits, Habitat & Types of Mice

A mouse is a small rodent with a pointed olfactory organ, furry round body, large ears and a long, often hairless, tail. There are hundreds of types of mice, divided into subfamilies of either Old World or New World species. Common varieties include deer mouse, house mouse, field mouse, wood mouse, dormouse, spiny mouse and zebra mouse.
Though some people talk about mice and rats every bit if they were the same thing, they are actually different types of animals in the rodent family. Rats generally are larger than mice, and they can be bald, scaly and cylinder-shaped.
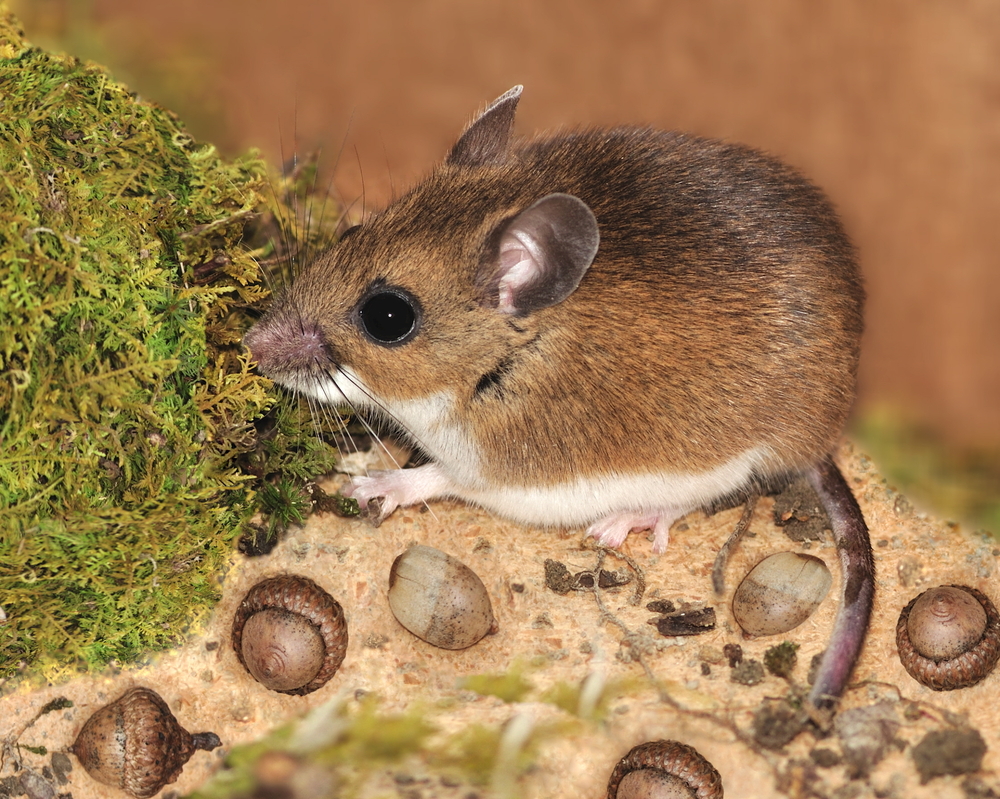

Size
Mice come up in a wide variety of colors and sizes. Some common mice colors are white, chocolate-brown and grey. Some are very tiny and others are effectually the size of a baked potato.
Mice typically abound from 1 to 7 inches (2.54 to 18 centimeters) in length and weigh between 0.v and 1 ounce (.23 to .028 kilograms). The African pygmy is the smallest known mouse on the planet. It measures 1.2 - three.i inches (3.04 to 7.874 cm) and can weigh less than .35 ounces (.01 kg). These measurements do non include tail length. Some mice have tails that are as long as their bodies.
Where do mice live?
Mice are hardy creatures that are found in nearly every state and type of terrain. They can live in forests, grasslands and manmade structures easily. Mice typically brand a burrow underground if they alive out in the wild. Their burrow helps protect them from predators. Their natural predators are cats, birds, wild dogs and foxes.
Mice are nocturnal, meaning they similar to sleep during the 24-hour interval. This is why pet mice or house mice can be heard playing or foraging during the night. Almost wild mice are timid toward humans and other animals, but they are very social with other mice. Domestic mice are very friendly toward humans and can make proficient pets for older children and adults.
According to the RSPCA, mice are very territorial. Even domestic mice similar to accept a large area that they tin claim as their own.
What do mice eat?
If you believe what you see in cartoons, you would think that mice eat cheese. Actually, they like to eat fruits, seeds and grains. They are omnivorous, which means they consume both plants and meat, and the common house mice will eat just nigh anything it tin can observe. In fact, if food is scarce, mice will even eat each other.
Mice have voracious appetites. They eat around 15 to xx times per day, so they build their homes nearby places that have readily attainable food sources.
Babe mice
When homes are infested with mice, humans volition often find chewed upwardly wires, books, papers and insulation around their habitation. Mice aren't eating these items, they are chewing them into pieces that they tin utilise to make their nests. This is because mice nests are made from whatever the female person mouse can find.
At around 4 to seven weeks erstwhile, a female mouse will mate and have immature. She will carry her young for 19 to 21 days and give birth to iv to a dozen babies, according to the University of Florida. Mice tin can accept a new litter of babies every three weeks.
Mice take unusual names. Females are does, males are bucks and babies are called pinkies because of their bright pinkish colour. Baby mice are as well called pups.
Pet mice can alive upwards to six years, while wild mice commonly only live around one to two.5 years.
Nomenclature/taxonomy
According to the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS), the taxonomy of mice is:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Form: Mammalia
- Order: Rodentia
- Suborder: Myomorpha
- Family: Muridae
- Subfamilies: Murinae (Sometime Earth rats and mice), Sigmodontinae (New World rats and mice)
- Genera & species: Hundreds, includingMus musculus (house mouse),Apodemus flavicollis (xanthous-necked field mouse),Apodemus sylvaticus (wood mouse),Peromyscus maniculatus (deer mouse),Micromys minutus (Eurasian harvest mouse) andMuscardinus avellanarius (hazel dormouse)
Conservation status:
Most mice accept healthy populations, though there are a few species that are endangered, such as the Alabama beach mouse. Massive hurricanes in past years have near wiped out their natural habitat. New Mexico's jumping mouse is likewise endangered due to wildfires, drought and other threats.
Other facts
Mice are much like humans in how their bodies and minds work. This is why laboratories use mice as exam subjects for medicines and other items that may be used on humans. Nearly all modern medicine is tested on mice before they go to human medical trials.
Mice are tough picayune creatures when they have their minds assault a crunchy scorpion snack. They can withstand multiple scorpion bites.
Mice can experience temperature changes and alterations in basis terrain through their whiskers.
While communicating with each other, mice make ultrasonic every bit well as regular sounds.
Most mice are very practiced jumpers. They tin can jump nearly 18 inches (46 cm) in the air. They also are talented climbers and swimmers.
A mouse'south heart tin can trounce 632 beats per minute. A human heart only beats threescore to 100 beats per infinitesimal.
A wood mouse volition shed its tail if the tail is caught by a predator.
Nina Sen contributed to this commodity.
Other resources:
- Humane Society of the Usa - Mouse
- BBC Nature - Mouse
- Orkin- Mouse Facts
What Size Opening Can A Mouse Get Through,
Source: https://www.livescience.com/28028-mice.html
Posted by: larsonoffichat1937.blogspot.com



0 Response to "What Size Opening Can A Mouse Get Through"
Post a Comment